MapReduce
Background
Problem for large service providers such as Google: computation requires hundreds or thousands of computers
- How do you distribute the computation?
- Distributing the computation boils down to distributing data
- Nodes fail, some nodes are slow, load balancing: difficult to make it work well
核心概念
A MapReduce framework (or system) is usually composed of three operations (or steps):
- Map: each worker node applies the
mapfunction to the local data, and writes the output to a temporary storage. A master node ensures that only one copy of the redundant input data is processed. - Shuffle: worker nodes redistribute data based on the output keys (produced by the
mapfunction), such that all data belonging to one key is located on the same worker node. - Reduce: worker nodes now process each group of output data, per key, in parallel.
# ("word", text) -> ("word", 1)
map(k1, v1) -> list(k2, v2)
# ("word", [1,1,2,3])-> ("word", 7)
reduce(k2, list(v2)) -> list(k2, v3)
map出来的东西再给reduce处理,task之间存在dependency
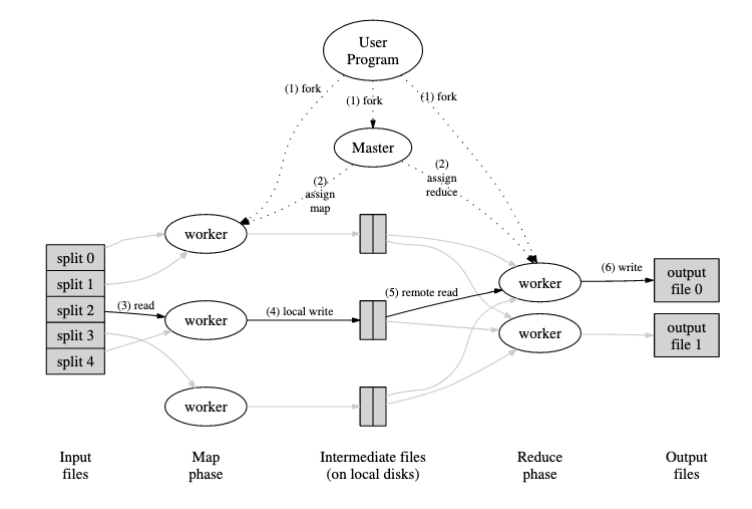
- The map component of a MapReduce job typically parses input data and distills it down to some intermediate result.
- The reduce component of a MapReduce job collates these intermediate results and distills them down even further to the desired output.
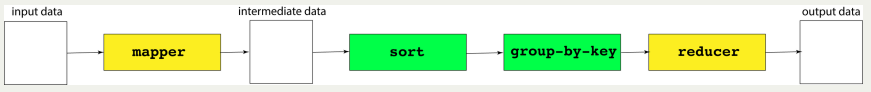
5步流程
Another way to look at MapReduce is as a 5-step parallel and distributed computation:
- Prepare the Map() input – the "MapReduce system" designates Map processors, assigns the input key K1 that each processor would work on, and provides that processor with all the input data associated with that key.
- Run the user-provided Map() code – Map() is run exactly once for each K1 key, generating output organized by key K2.
- "Shuffle" the Map output to the Reduce processors – the MapReduce system designates Reduce processors, assigns the K2 key each processor should work on, and provides that processor with all the Map-generated data associated with that key.
- Run the user-provided Reduce() code – Reduce() is run exactly once for each K2 key produced by the Map step.
- Produce the final output – the MapReduce system collects all the Reduce output, and sorts it by K2 to produce the final outcome.
优点
即使编程人员不了解分布式计算框架的内部运行机制,只要够参照 Map 和 Reduce 的思想描述清楚要处理的问题,即编写 map 函数和 reduce 函数,就可以轻松地实现大数据的分布式计算。
对于复杂的编程需求,只需参照 MapReduce的接口,可以完成海量数据的处理。
总结
Map中的每一个key都是可以并行的
框架会把相同的k2给同一个reduce处理
Example
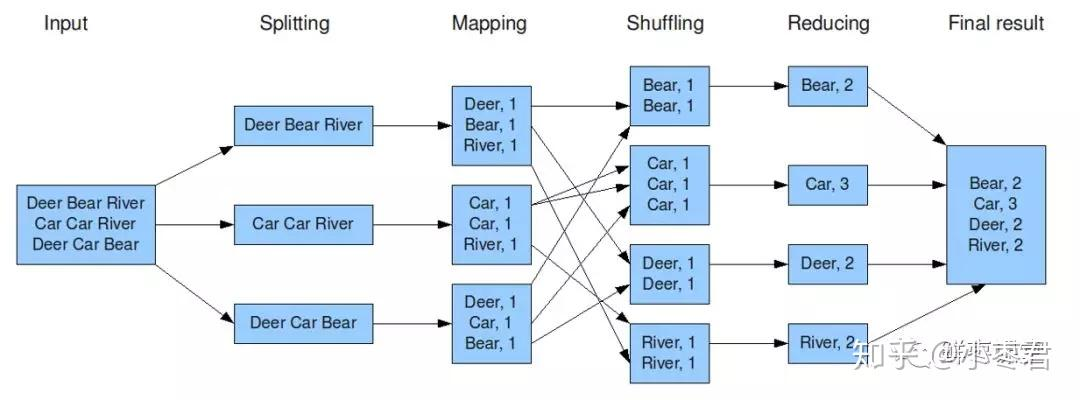
Simple example of word count (wc):
map(String key, String value):
# key: document name
# value: document contents
for word w in value:
EmitIntermediate(w,"1")
reduce(String key, List values):
# key: a word
# values: a list of counts
int result = 0
for v in values:
result += ParseInt(v)
Emit(AsString(result))
input:
"The number of partitions (R) and the partitioning function are specified by the user."
map:
("the", "1") , ("the", "1"), ("The", "1"), ("of", 1), (number, "1"), ...
reduce:
"the", ("1", "1") -> "2"
"The", ("1") -> "1"
"of", ("1") -> "1"
"number", ("1") -> "1"
Reference
MapReduce - Wikipedia
cs110-lecture-17-mapreduce.pdf (stanford.edu)
MapReduce分布式计算框架的优缺点 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)